skrub.to_datetime#
- skrub.to_datetime(data, format=None)[source]#
- skrub.to_datetime(df, format=None)
- skrub.to_datetime(df, format=None)
- skrub.to_datetime(df, format=None)
- skrub.to_datetime(column, format=None)
- skrub.to_datetime(column, format=None)
Convert DataFrame or column to Datetime dtype.
- Parameters:
- datadataframe or column
The dataframe or column to transform.
- format
strorNone, optional, default=None Format string to use to parse datetime strings. See the reference documentation for format codes: https://docs.python.org/3/library/datetime.html#strftime-and-strptime-format-codes .
Examples
>>> import pandas as pd >>> from skrub import to_datetime >>> X = pd.DataFrame(dict(a=[1, 2], b=["01/02/2021", "21/02/2021"])) >>> X a b 0 1 01/02/2021 1 2 21/02/2021 >>> to_datetime(X) a b 0 1 2021-02-01 1 2 2021-02-21
Examples using skrub.to_datetime#
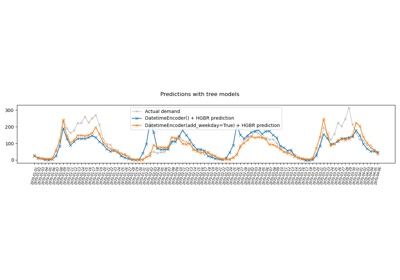
Handling datetime features with the DatetimeEncoder
Handling datetime features with the DatetimeEncoder